In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have rapidly evolved, becoming more sophisticated and integral to various applications across industries. With the most recent updates being Apple Intelligence, GPT-4o, and Gemini. As we navigate through 2024, several trends in LLM bots are emerging that are poised to shape the future of artificial intelligence and its interaction with humans. Let’s dive into 10 key trends in AI for 2024 that are defining the landscape of LLM bots.

1. Hyper-Personalization
Personalization has always been a significant goal for AI-driven services, but with advancements in LLM Chat GPT technology, we’re seeing unprecedented levels of customization. LLM bots are now capable of tailoring interactions to individual user preferences, behaviors, and needs with incredible accuracy. This trend is evident in customer service, where an LLM chatbot can recall past interactions and predict future needs, providing a seamless and highly personalized experience. Below is an example of personalization done in 2 steps with Teneo.
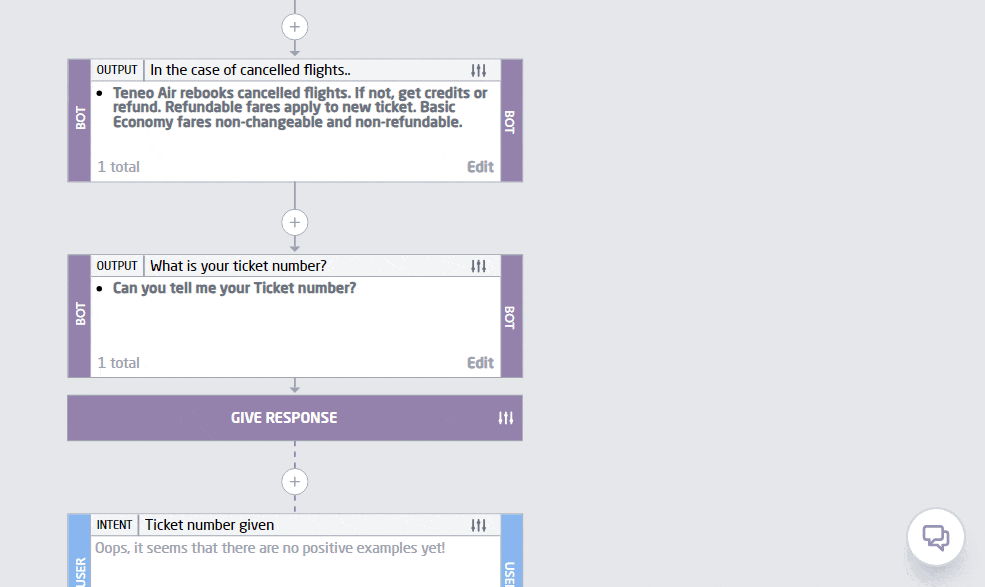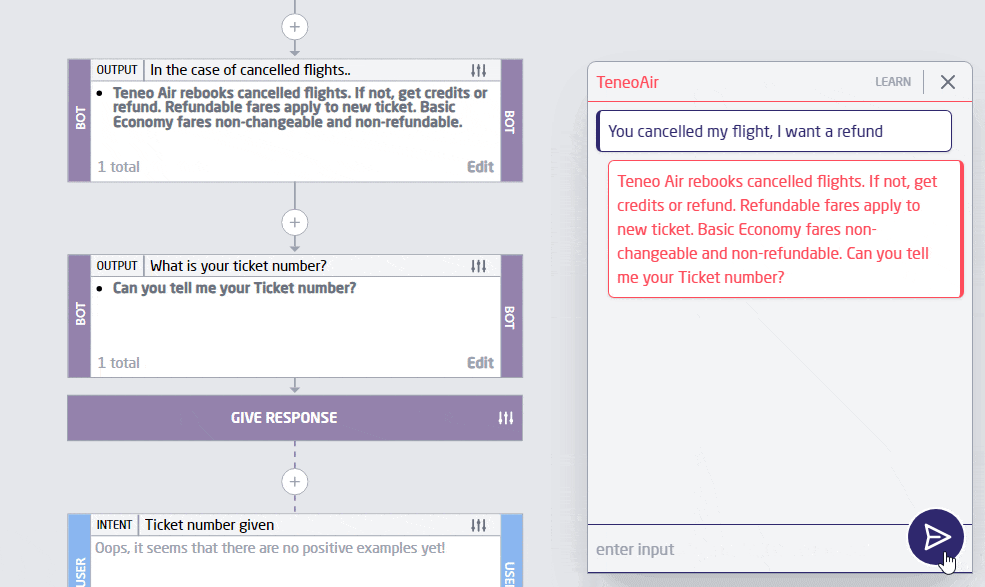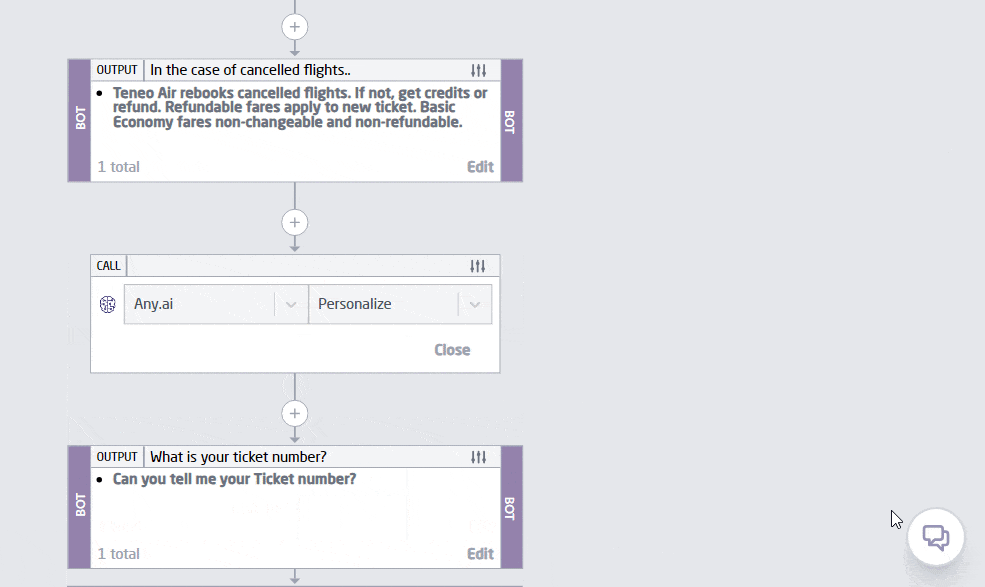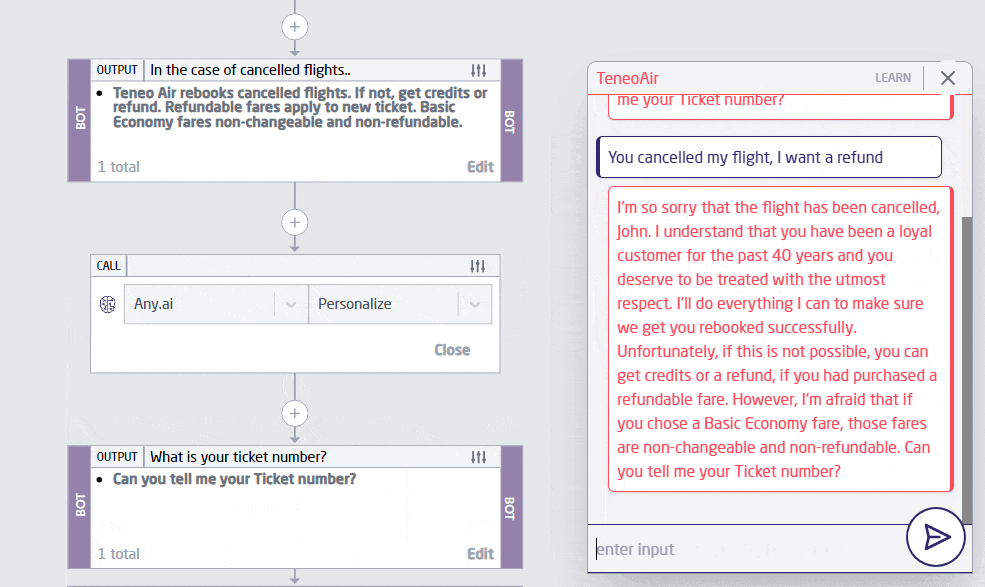
2. Multimodal Capabilities
Traditionally, LLM bots have been primarily text-based. However, the latest models are now integrating multimodal capabilities, combining text, audio, visual data, and even sensory data to create a more comprehensive interaction experience. For instance, a customer service bot can now understand and respond to queries through voice, recognize emotions from facial expressions, and interpret images to assist users more effectively. This multimodal approach enhances the bot’s ability to interact in more human-like and intuitive ways, bridging the gap between digital and real-world interactions.
3. Ethical AI and Bias Mitigation
As LLM bots become more ingrained in everyday applications, the importance of ethical AI practices has grown. There is a strong focus on developing models that are fair, transparent, and free from bias. Researchers and developers are investing in methods to identify and mitigate biases in training data, ensuring that LLM chat GPT systems make decisions that are equitable and just.
4. Enhanced Conversational Abilities
The conversational abilities of LLM bots are becoming increasingly nuanced and sophisticated. Advanced models can now maintain context over long conversations, understand complex queries, and provide more natural and human-like responses. This trend is transforming industries such as mental health support, where an LLM chatbot can engage in meaningful dialogues and provide real-time assistance to users.
5. Integration with external APIs
The integration of LLM bots with external APIs and other products is another emerging trend. By connecting to various smart devices, LLM chat systems can offer more holistic solutions. For instance, a smart home assistant powered by an LLM can control household appliances, provide weather updates, and even offer personalized recommendations based on user habits and preferences. Teneo has over 50 open sourced connectors with other software, and allows you to integrate your LLM with these.

6. Scalability and Deployment in Diverse Environments
LLM bots are increasingly being designed for scalability and deployment across diverse environments, from small businesses to large enterprises. Advances in cloud computing and edge AI are enabling LLM bots to operate efficiently even in resource-constrained settings. This scalability ensures that businesses of all sizes can leverage the power of LLM chat systems to enhance their operations and customer engagement.
7. Improved Accessibility
Accessibility is a key focus, with LLM bots being developed to cater to users with disabilities. Features such as voice-to-text, text-to-speech, and visual recognition are being enhanced to provide an inclusive experience. This trend is particularly impactful in education and healthcare, where LLM Chat GPT can assist users with various needs, ensuring equitable access to information and services.
8. Proactive and Predictive Interactions
Gone are the days when bots merely reacted to user inputs. The latest LLM bots are increasingly proactive and predictive. They can anticipate user needs and provide suggestions before they are even asked. This trend is powered by advanced machine learning algorithms that analyze user behavior patterns to offer timely and relevant assistance.
9. Cross-Lingual and Multilingual Support
As global communication becomes more interconnected, the demand for cross-lingual and multilingual LLM bots is rising. Advanced models can now fluently converse in multiple languages, breaking down language barriers and facilitating smoother interactions in international contexts. This capability is particularly beneficial for global customer support and international collaborations. Teneo is natively supporting +86 languages, and is able to use any LLM for automatic translation.

10. Increased Collaboration with Human Agents
Rather than replacing human agents, LLM bots are increasingly seen as collaborative partners. In customer service, for instance, LLM chatbots handle routine inquiries, allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues. This collaboration enhances efficiency and ensures that customers receive high-quality service. Teneo can be used as a layer before reaching a live agent, thank to its Smart Agent Handover, helping the user with things that could be automatized, leaving the critical things for the live agent.

Stay Ahead of the Curve with Teneo
Ready to leverage the latest trends in LLM bots and stay ahead of your competition? Teneo offers cutting-edge solutions that encompass hyper-personalization, multimodal capabilities, ethical AI practices, and more. Experience firsthand how Teneo’s advanced LLM chat and LLM chatbot technology can transform your business operations, enhance customer engagement, and drive innovation.
Book a demo with Teneo today and discover how our comprehensive AI solutions can help you keep up with the latest trends and take your business to the next level. Don’t miss out on the future of intelligent automation – click the link below to schedule your personalized demo now!
FAQ
1. What is hyper-personalization in LLM bots?
Hyper-personalization in LLM bots refers to the advanced customization of interactions based on individual user preferences, behaviors, and needs. Utilizing sophisticated AI algorithms, LLM bots can recall past interactions, predict future needs, and tailor responses to provide a seamless and highly personalized user experience. This trend is particularly evident in customer service, where bots can offer personalized recommendations and solutions.
2. How do multimodal capabilities enhance LLM bots?
Multimodal capabilities allow LLM bots to process and respond to a combination of text, audio, visual data, and even sensory inputs. This integration enables bots to understand voice commands, recognize emotions from facial expressions, and interpret images, creating a more comprehensive and human-like interaction experience. This approach is beneficial in various applications, from customer service to healthcare, where understanding multiple forms of input can improve assistance and outcomes.
3. Why is ethical AI and bias mitigation important in LLM bots?
As LLM bots become more prevalent, ensuring they operate fairly and transparently is crucial. Ethical AI practices focus on developing models that are free from biases that could lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Researchers and developers are actively working on identifying and mitigating biases in training data to ensure that LLM bots make equitable and just decisions, fostering trust and reliability in AI systems.
4. How do proactive and predictive interactions work in LLM bots?
Proactive and predictive interactions involve LLM bots anticipating user needs and providing suggestions or actions before being explicitly asked. This capability is powered by advanced machine learning algorithms that analyze user behavior patterns. For instance, an LLM chatbot can predict and address frequently asked questions, recommend products, or remind users of upcoming tasks, thus improving efficiency and user satisfaction.

